How it works
Dynamic tables
Queues in YTsaurus
A distributed, replicated message log based on dynamic tables, with support for sharding and cross-cluster replication, and compatible with the Apache Kafka protocol.
Flexible table-based storage
Export messages to a static table for long-term storage, and delete them via TTL after processing
An all-in-one transaction space
With a single transaction space with dynamic tables, you can process events exactly-once without complex integrations and third-party tools
Scalability and fault tolerance
Sharding and distributed storage allow you to scale the system horizontally without a single point of failure
Data processing: Scheduler
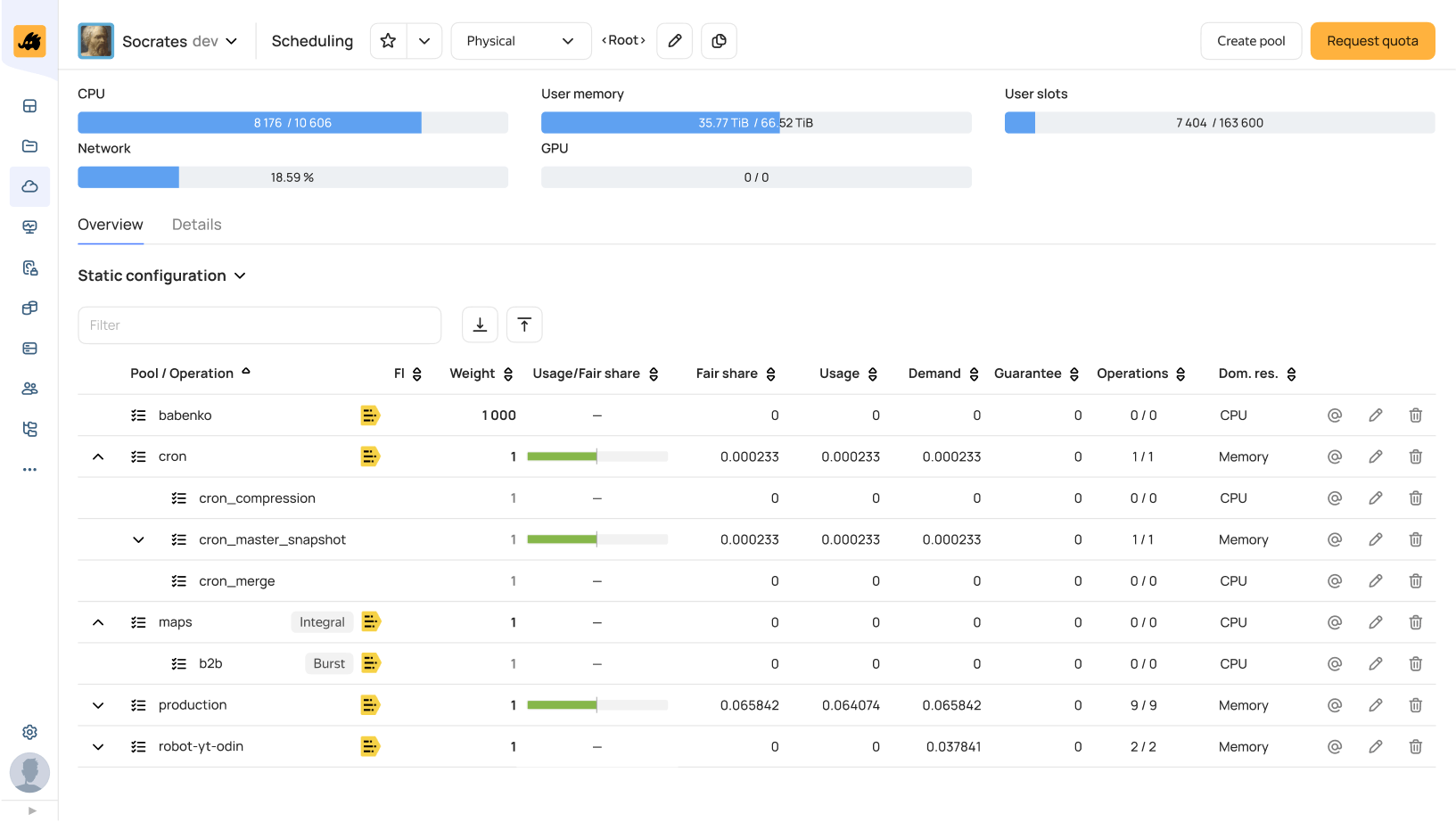
Operations on the cluster can be started with YQL, a dialect of SQL with UDF, window functions and more. You can use it to build complex data processing pipelines that store subqueries in variables and create chains of dependent queries.
CHYT allows you to launch ClickHouse® clusters to work with data in YTsaurus. It can operate as a data source for visualization and BI tools, making it excellent for ad hoc queries.
SPYT clusters run Apache Spark inside YTsaurus Vanilla operations. They are great for building ETL pipelines.
What is YTsaurus?
Try YTsaurus

.png)
.png)